What is a factor market?
A factor market is a place where businesses can buy the manufacturing factors or assets they need to make their goods and services. The input market is another term for this market.

Source: © Walstraasworld | Megapixl.com
Summary
- A factor market is the place where production factors can be bought and sold.
- The commodity industry's demand drives the factor market.
- The labour market is a key element of the factor market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does the factor market play in the economy?
A factor market is a public marketplace where people can buy and sell production factors. Everyone can participate.
The process of transforming raw materials into finished goods is considered as production. Factor markets are where companies get their inputs.
In the manufacturing process, labour is the most crucial element. Employees provide the supply in the labour market, while businesses provide the demand.
Wages paid by businesses to employees are part of the factor market. This market includes investors who earn some compensation, such as dividends or rental payments. Households become sellers because of the money paid for their services by the customers, who are companies. Households provide labour to businesses, which, in turn, pay them wages that are used to purchase goods and services from the same businesses. A money flow closed loop is created when the factor markets as well as the goods and services markets are combined.
The price of each factor is regulated by supply and demand. The demand, on the other hand, is derived because it is based on production demand. As a result, the amount of input is determined by how much a business produces.
Wages will increase in a thriving economy with a tight labour market because demand for workers is strong. Hence, when a commodity is in high demand, a company can expand its workforce.
In contrast, wages can stagnate or even decline during a recession when unemployment rises, and demand for goods is limited. To cope with the drop in demand, companies can reduce hiring and even lay off staff.
What are the factors influencing production?
To manufacture products and deliver services, resources would be utilized in the production process. Production factors are sometimes referred to as "resources." The key factors are entrepreneurship, labour, capital and land. To generate a given output, different proportions of production factors can be combined.
Labour market - The factor market is incomplete without the labour market. The majority of goods and services require human input, and labour is traded on a contract basis, known as a job; however, some labour is traded regularly, known as casual labour. Human capital refers to a person's abilities gained through education, knowledge, and practice.
Collective bargaining by trade unions, or a government's decision to enforce a minimum wage or interfere in another law, affects the labour market.
Land market - All the natural resources that have been provided to us, such as water, air, natural gas, minerals, oil, coal, and so on, are referred to as "land."
Capital market - Capital refers to the funds that companies use to purchase and run their production processes. People lend and invest in this market to boost the value of capital goods.

Source: © Adam1975 | Megapixl.com
Entrepreneurship - Entrepreneurship is a factor that generates businesses and employs other factors.
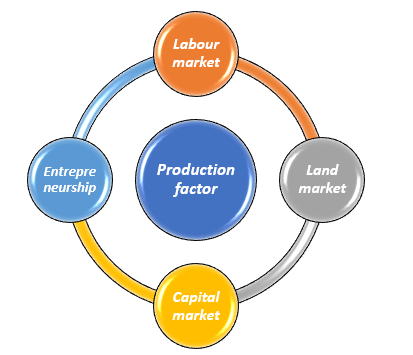
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
How does a factor market work?
The demand in the commodity industry drives factor markets. There would be no need for machines, rubber and people who conceptualize, design, and produce motorcycles if hardly anyone in the world wanted to buy one. However, if there is a sudden surge in demand for motorcycles, the demand for the materials used to produce motorcycles would rise.
Derived demand is another name for the concept. When the requirement for resources used to complete finished goods or services is generated from the demand for such products or services, it is known as derived demand.
The factor market is a form of market economy that operates inside capitalism. It is supported in a market economy, and the distribution of factor capital is left to the market.
How does the factor market differ from the product market?
Companies that buy raw materials and labour to make final products sold to customers make up the factor market. It also includes consumers. When a customer applies for a job, they function as a seller because they are selling their services. The organization employs them - it is a buyer, as it is purchasing labour.
Companies serve as suppliers, offering their goods to potential buyers at prices determined by the dynamics of supply and demand in the product market. Government and other agencies also intervene to monitor market activity, and the market can be classified as free or regulated depending on the degree of control imposed.
A factor market differs from a product or output market, a market for finished goods or services. Households are buyers in this case, whereas companies are sellers. In a factor market, however, households sell, and companies purchase. It is usually a business-to-business transaction in the factor market and a business-to-person transaction in the product market.
Factor markets and product markets are distinguished by the fact that factor markets include sources of production such as labour and capital, whereas product markets are markets for goods. When customers demand more products and services, suppliers demand more efficient capital to manufacture those goods and services.
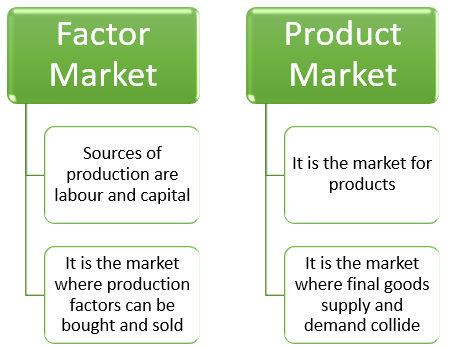
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What impact does the factor market have?
A solid understanding of the factor market is essential for making good stock market investments. When evaluating a company's future potential, it is critical to consider real competitors in its final-product market and developments in its factor markets and their possible impact on future success.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...